Cardboard is a widely used material in packaging, shipping, and a variety of industrial applications. Understanding the price trends of cardboard is crucial for manufacturers, retailers, and stakeholders in the packaging industry. This article provides a comprehensive analysis the cardboard price trend analysis, covering historical data, recent fluctuations, market dynamics, and future outlook.
Historical Price Trends
Early 2000s to 2010
From the early 2000s to 2010, the price of cardboard exhibited moderate fluctuations. Key factors influencing prices during this period included:
- Raw Material Costs: The primary raw materials for cardboard production are paper and pulp. Fluctuations in the prices of these raw materials directly impacted cardboard prices.
- Industrial Demand: Growing demand from the packaging and shipping sectors drove price trends.
- Economic Conditions: Global economic conditions, including inflation rates and currency fluctuations, played a role in shaping cardboard prices.
2010 to 2020
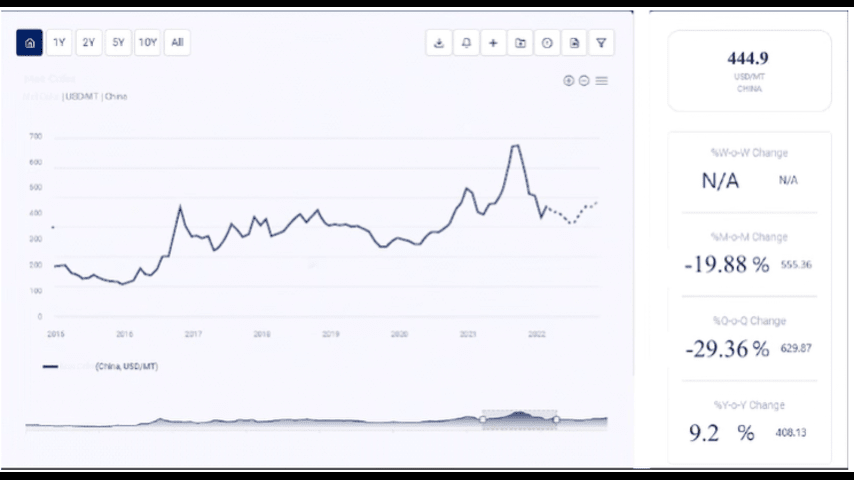
Between 2010 and 2020, cardboard prices showed moderate volatility, generally stabilizing between $400 and $800 per metric ton. Key factors during this period included:
- Increased Demand: Expanding e-commerce and retail sectors increased demand for cardboard packaging.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in production technologies and efficiencies helped stabilize prices.
- Regulatory Policies: Environmental regulations promoting recycling and sustainable sourcing of raw materials positively impacted demand and pricing.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cardboard-price-trends/pricerequest
Recent Price Trends (2020-2023)
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on global markets, including cardboard. In early 2020, prices fell due to reduced industrial activity and disruptions in supply chains. However, as demand for packaging materials surged due to increased online shopping and home deliveries, cardboard prices rebounded.
2021 to 2023
From 2021 onwards, cardboard prices experienced significant fluctuations, influenced by the following factors:
- Raw Material Shortages: Supply chain disruptions and raw material shortages, particularly of paper and pulp, led to price increases.
- Rising Production Costs: Increased costs of energy, transportation, and labor contributed to higher production costs, which were reflected in market prices.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations in key markets, such as the European Union, drove demand for recycled and sustainably sourced cardboard.
- Economic Recovery: As economies recovered from the pandemic, increased industrial activity and consumer spending boosted demand for cardboard packaging.
Market Dynamics
Supply Factors
The supply of cardboard is influenced by several key factors:
- Raw Material Availability: The availability and cost of raw materials like paper and pulp significantly impact production costs and supply levels.
- Production Capacity: The capacity of manufacturing facilities to produce cardboard affects supply. Investments in new plants or expansions of existing ones can increase supply.
- Geopolitical Stability: Political stability in regions producing key raw materials and cardboard itself can affect supply chains and prices.
Demand Factors
Demand for cardboard is driven by its applications in various sectors:
- E-commerce: The rise of e-commerce has significantly increased the demand for cardboard packaging for shipping and delivery purposes.
- Retail: Cardboard is widely used in retail packaging for products such as electronics, clothing, and food.
- Industrial Applications: Cardboard is used in industrial packaging for protecting and transporting machinery, equipment, and other goods.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the cardboard market:
- Production Efficiency: Innovations in production technologies can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and lower production costs.
- Recycling Technology: Advances in recycling technology can increase the supply of recycled cardboard and reduce dependence on virgin raw materials.
- Sustainable Practices: Development of sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly inks and adhesives, can improve the environmental footprint of cardboard production.
Environmental and Regulatory Impact
Environmental and regulatory factors significantly influence the cardboard market:
- Sustainability Initiatives: Increasing focus on sustainability and environmental protection has led to greater demand for recycled and sustainably sourced cardboard.
- Recycling Mandates: Regulations promoting recycling and the use of recycled materials impact the supply and pricing of cardboard.
- Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Certification: Compliance with FSC standards ensures that cardboard is sourced from responsibly managed forests, affecting supply and costs.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for cardboard prices is influenced by several factors:
- Technological Innovations: Continued advancements in production technologies and new applications will drive market growth and impact pricing.
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic recovery and growth, especially in developing markets, will drive demand for cardboard in e-commerce, retail, and industrial applications.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives will promote the use of recycled and sustainably sourced cardboard.
- Raw Material Supply: Ensuring a stable supply of key raw materials like paper and pulp will be crucial for maintaining stable production costs and pricing.
Conclusion
The cardboard market is characterized by its sensitivity to various economic, environmental, and regulatory factors. Understanding the historical and recent price trends, along with the underlying market dynamics, is crucial for stakeholders to navigate this complex landscape. As technological advancements and sustainability initiatives continue to evolve, the cardboard market will face new opportunities and challenges. By staying informed and adapting to these changes, manufacturers, buyers, and policymakers can better manage the impacts of fluctuating cardboard prices.